Suppose you solve the profit maximization problem for a single-input, price-taking producer whose technology is given by 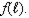 The labor demand function is
The labor demand function is 
a. Suppose
src="https://sciemce.com/media/3/ppg__cognero__Chapter_11_One_Input_and_One_Output_A_Short_Run_Producer_Model__media__59179cfd-ca3e-489f-aabb-5a92da40ce1d.PNG" style="vertical-align: -13px;" width="79px" height="38px" align="absmiddle" /> Might 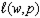 in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain.
in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain.
b. Suppose 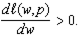 Might
Might 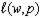 in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain.
in fact be the correct labor demand function? Explain.
c. Intuitively explain how (b) might arise from the profit maximization problem.
What will be an ideal response?
a. Yes -- labor demand functions in face ought to tell us that an increase in wage causes a reduction in labor hired.
b. No -- this would mean the labor demand curve slopes up, which is not possible.
c. This can emerge in a profit maximization problem if the producer choice set is non-convex. For instance, if 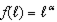 , the first order conditions give us
, the first order conditions give us
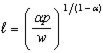 .
.
If 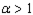 ,
, 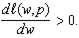 In a graph, this happens when we have identified a production plan that lies at a tangency that is a local minimum.
In a graph, this happens when we have identified a production plan that lies at a tangency that is a local minimum.
Economics
src="https://sciemce.com/media/3/ppg__cognero__Chapter_11_One_Input_and_One_Output_A_Short_Run_Producer_Model__media__59179cfd-ca3e-489f-aabb-5a92da40ce1d.PNG" style="vertical-align: -13px;" width="79px" height="38px" align="absmiddle" /> Might 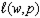
b. Suppose 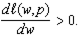
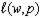
c. Intuitively explain how (b) might arise from the profit maximization problem.
What will be an ideal response?
b. No -- this would mean the labor demand curve slopes up, which is not possible.
c. This can emerge in a profit maximization problem if the producer choice set is non-convex. For instance, if
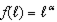 , the first order conditions give us
, the first order conditions give us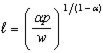 .
.If
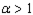 ,
, 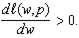 In a graph, this happens when we have identified a production plan that lies at a tangency that is a local minimum.
In a graph, this happens when we have identified a production plan that lies at a tangency that is a local minimum.You might also like to view...
A tax imposed by a government on imports of a good into a country is called a
A) tariff. B) value added tax. C) sales tax. D) quota.
If a bond's coupon adjusts to pay a constant real rate of return, then an increase in inflation would cause
A) the nominal coupon payment to rise. B) the nominal coupon payment to fall. C) the nominal coupon payment to remain unchanged. D) the bond's price to fluctuate wildly.
In the principal-agent model, at the employee's optimal effort choice:
A. the incentive coefficient of effort is very high. B. the net benefits of effort are maximized. C. the marginal benefit of effort is negative. D. the marginal costs of efforts exceed the marginal revenue.
In a perfectly competitive industry, in the long run:
A. firms earn a positive economic profit. B. firms earn zero economic profit. C. firms earn a negative economic profit. D. firms might earn a positive, zero, or negative economic profit.