Explain the differences between discretionary fiscal policy and automatic stabilizers, and give one example of each
What will be an ideal response?
Discretionary fiscal policy is government policy that involves deliberate changes in taxes, transfer payments or government expenditures to achieve macroeconomic policy objectives. Examples of discretionary fiscal policy include the government enacting tax cuts, increasing the duration of unemployment benefits, and increasing spending on infrastructure projects during a recession in an attempt to increase output and employment.
Automatic stabilizers refer to changes in taxes, transfer payments, or government expenditures that automatically occur with the business cycle. Examples of automatic stabilizers include the natural decrease in tax revenues and the natural increase in unemployment payments that occur during a recession.
You might also like to view...
Using the Figure 13.3 above explain why this firm could not possibly represent a monopolist. What type of firm is represented by this graph and why?
What will be an ideal response?
In 2010, fears were growing that the dollar would experience a significant decline in value. What are the likely implications for the euro-dollar exchange rate?
What will be an ideal response?
About ______ percent of China's population lives in rural areas.
A. 5 B. 25 C. 50 D. 67
Answer the question based on the information given in the table below that shows the items and figures taken from a consolidated balance sheet of the twelve Federal Reserve Banks. All figures are in billions of dollars.
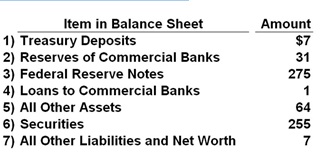
In the balance sheet above for the Federal Reserve, the assets would be items 5 and:
A. 1 and 2
B. 2 and 3
C. 3 and 4
D. 4 and 6