A curve that describes the relationship between the price of a good and the amount a particular consumer purchases (holding the consumer's income, preferences and all other prices fixed) is called:
A. a price-consumption curve.
B. an individual demand curve.
C. an income-consumption curve.
D. a budget line.
B. an individual demand curve.
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph of the demand for steak to answer the question below.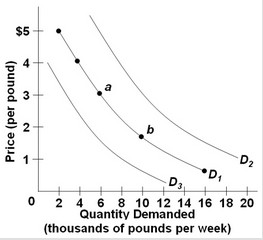 Refer to the above diagram and assume that steak is a normal good. Which of the following would shift the demand for steak from D1 to D3?
Refer to the above diagram and assume that steak is a normal good. Which of the following would shift the demand for steak from D1 to D3?
A. a decrease in consumer incomes B. a decrease in the price of steak C. an increase in consumer incomes D. an increase in the price of steak
In the fooling model's AD/SAS/LAS diagram, short-run equilibria to the right of the LAS curve require the price level to be
A) above what workers expect. B) above what firms expect. C) below what workers expect. D) below what firms expect.
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A. The supply of money decreases when the Federal Reserve Banks buy government securities from households or businesses. B. Excess reserves are the amount by which actual reserves exceed required reserves. C. Commercial banks increase the supply of money when they purchase government bonds from households or businesses. D. Commercial bank reserves are an asset to commercial banks but a liability to the Federal Reserve Banks.
A firm facing a ________ demand curve, ceteris paribus, will have zero quantity demanded if it raises its price above the market price.
A. perfectly elastic B. relatively inelastic C. perfectly inelastic D. relatively elastic