The marginal propensity to consume is:
A. the change in consumer spending minus the change in aggregate disposable income.
B. the change in consumer spending divided by the change in aggregate disposable income.
C. the proportion of total disposable income that the average family consumes.
D. increasing if the marginal propensity to save is increasing.
B. the change in consumer spending divided by the change in aggregate disposable income.
You might also like to view...
When a perfectly competitive, well-functioning market is in equilibrium:
A. total surplus is maximized. B. the market is efficient. C. deadweight loss is zero. D. All of these are true.
Which of the following scenarios best illustrates the concept of cyclical unemployment?
a. Grace loses her job because of new automated machinery. b. Sean quits his job to look for work that is more fun. c. Ellen quits looking for work because she doesn't think she can find a suitable job. d. Marian loses her job because of a recession.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD3 the result in the long run would be: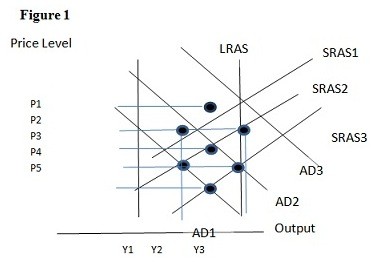
A. P2 and Y2. B. P1 and Y2. C. P4 and Y2. D. P1 and Y1.
The marginal revenue of a monopolist falls below price because the firm
A. Has an upward-sloping marginal cost curve. B. Confronts a downward-sloping demand curve. C. Faces a market demand curve that is inelastic. D. Is not limited by market demand.