If a wave's frequency doubles and its speed stays constant, its wavelength
A) becomes 16× longer.
B) is also doubled.
C) is unchanged, as c is constant.
D) is now 4× longer.
E) is halved.
E
You might also like to view...
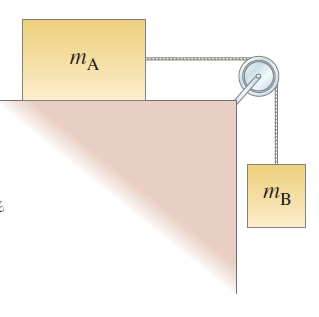
Figure 4–53 shows a block (mass mA) on a smooth horizontal surface, connected by a thin cord that passes over a pulley to a second block which hangs vertically.
(a) Draw a free-body diagram for each block, showing the force of gravity on each, the force (tension) exerted by the cord, and any normal force.
(b) Apply Newton’s second law to find formulas for the acceleration of the system and for the tension in the cord. Ignore friction and the masses of the pulley and cord.
If someone were to suggest that possibly half of the galaxies in the universe are composed of antiparticles ("anti-galaxies"), what argument(s) might you present to refute this hypothesis?
(Remember, atoms made of antiparticles have the same chemical and spectroscopic properties that our "ordinary" matter has.)
Identical point charges (+30 ?C) are placed at the corners of a rectangle (4.0 m × 6.0 m). How much external energy is required to bring a charge of 55 ?C from infinity to the midpoint of one of the 6.0-m long sides of the rectangle?
a. 22 J b. 16 J c. 13 J d. 19 J e. 8.0 J
Why is it important for a chemist to know the relative masses of atoms?
A) There are not that many different kinds of atoms and so it's important to know how they relate to one another. B) It provides information about how many atoms two samples have relative to each other. C) It provides an indication of how the different atoms will interact. D) Because the mass of an atom is directly related to its chemical properties.