Sort these materials in order of increasing dielectric constant: paper, vacuum, air
What will be an ideal response?
vacuum, air, paper
You might also like to view...
The graph below shows the velocity versus time graph for a ball. Which explanation best fits the motion of the ball as shown by the graph?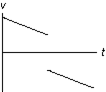
A. The ball is falling, is caught, and is thrown down with greater velocity. B. The ball is rolling, stops, and then continues rolling. C. The ball is rising, hits the ceiling, and falls down. D. The ball is falling, hits the floor, and bounces up. E. The ball is rising, is caught, and then is thrown down.
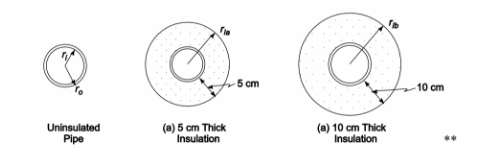
A salesperson for insulation material claims that insulating exposed steam pipes in the basement of a large hotel will be cost effective. Suppose saturated steam at 5.7 bars flows through a 30-cm- OD steel pipe with a 3 cm wall thickness. The pipe is surrounded by air at 20°C. The convective heat transfer coefficient on the outer surface of the pipe is estimated to be 25 W/(m2 K). The cost of generating steam is estimated to be $5 per 109 J and the salesman offers to install a 5 cm thick layer of 85% magnesia insulation on the pipes for $200/m or a 10-cm-thick layer for $300/m. Estimate the payback time for these two alternatives assuming that the steam line operates all year long and make a recommendation to the hotel owner. Assume that the surface of the pipe as well as the
insulation have a low emissivity and radiative heat transfer is negligible.
GIVEN
Steam pipe in a hotel basement
Pipe outside diameter (Do) = 30 cm = 0.3 m
Pipe wall thickness (Ls) = 3 cm = 0.03 m
Surrounding air temperature (T?) = 20°C
Convective heat transfer coefficient (hc) = 25 W/(m2 K)
Cost of steam = $5/109J
Insulation is 85% magnesia
FIND
Payback time for
(a) Insulation thickness (LIa) = 5 cm = 0.05 m; Cost = $200/m
(b) Insulation thickness (LIb) = 10 cm = 0.10 m; Cost = $300/m
Make a recommendation to the hotel owner.
ASSUMPTIONS
The pipe and insulation are black (? = 1.0) The convective resistance on the inside of the pipe is negligible, therefore the inside pipe surface temperature
is equal to the steam temperature The pipe is made of 1% carbon steel Constant thermal conductivities
SKETCH
When something is thrown over large distances (on Earth), what new factor comes into play?
a. The curvature of the Earth. b. The increase in gravity over long distances. c. The decrease in gravity over long distances. d. The tendency of thrown objects to fall to the ground. e. The difference between miles and kilometers.
Describe the fate of planet Earth if the Sun were to collapse to a black hole
What will be an ideal response?