Briefly discuss the role of moral hazard in risk.
What will be an ideal response?
An information problem associated with the insurance market is called moral hazard. If an individual is fully insured for fire, theft, auto, life, and so on, what incentives will this individual have to take additional precautions to mitigate risk? For example, a person with auto insurance may drive less cautiously than would a person without auto insurance. Insurance companies try to remedy the adverse selection problem by requiring regular checkups, providing discounts for nonsmokers, charging different deductibles and different rates for different age and occupational groups, and so on. Additionally, those with health insurance may devote less effort and resources to staying healthy than those who are not covered. The problem, of course, is that if the insured are behaving more recklessly than they would if they were not insured, the result might be much higher insurance rates. The moral hazard arises from the fact that it is costly for the insurer to monitor the behaviors of the insured party to detect if a product failure was the consequence of a manufacturing defect or the abuse of the owner-user.
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph of the demand for pasta to answer the question below.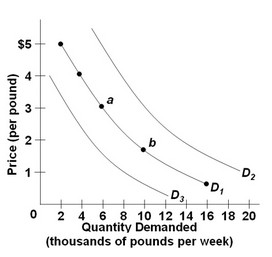 Refer to the three demand curves for pasta and assume that pasta is an inferior good. Which of the following would shift the demand for pasta from D1 to D3?
Refer to the three demand curves for pasta and assume that pasta is an inferior good. Which of the following would shift the demand for pasta from D1 to D3?
A. an increase in the price of pasta B. a decrease in consumer incomes C. an increase in consumer incomes D. a decrease in the price of pasta
In the 1960s, many economists and policymakers believed the trade-off between inflation and unemployment was permanent
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Suppose a market with a Cournot structure has five firms and a market price elasticity of demand equal to -2. What is a Cournot firm's Lerner Index?
A) .1 B) .2 C) .5 D) 1
To keep high inflation from eroding the value of money, monetary authorities in the United States
A. control the supply of money in the economy. B. create token money that is less than its intrinsic value. C. establish insurance on checkable deposit accounts. D. make paper money legal tender for the payment of debt.