Normative economics
A. predicts the consequences of alternative actions.
B. is the focus of most modern economic reasoning.
C. answers the question "What ought to be?"
D. answers the question "What is?"
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
According to the table shown, what is the firm's marginal revenue from the 3rd unit produced?
This table shows the total costs for various levels of output for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market.
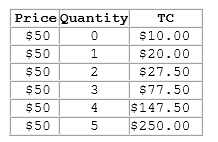
A. $50
B. $90
C. $150
D. $60
Which of the following is true of U.S. net exports prior to the 1960s?
a. Since most of the oil needs of the U.S. were met through imports, imports exceeded exports prior to the 1960s in the U.S. b. Prior to the 1960s, exports from the U.S. more or less equalled imports into the U.S. c. The U.S. was running a trade surplus prior to the 1960s. d. Prior to the 1960s, the U.S. ran twin deficits- both a current account deficit as well as a budget deficit. e. Since the U.S. dollar was overvalued prior to the 1960s, the U.S. neither exported nor imported any goods and services.
Camille is at the candy store with her grandmother, who offers to buy her $6 worth of candy. If lollipops are $1 each and candy bars are $2 each, what combination of candy can Camille's grandmother buy for her?
A. Six lollipops and three candy bars. B. Two lollipops and two candy bars. C. Three lollipops and two candy bars. D. One lollipop and three candy bars.
In a growing economy, __________ enjoy a rising standard of living.
A. only the rich B. both rich and poor C. neither the rich nor the poor D. only the poor