Equilibrium price differentials for productive resources:
A. Tend to be self-eliminating
B. May be caused by differences in the quality of those resources
C. Are eliminated when the allocation of resources is in a state of equilibrium
D. Are unrelated to differences in nonmonetary benefits
B. May be caused by differences in the quality of those resources
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph of the bicycle market to answer the question below.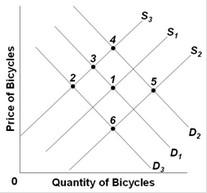 S1 and D1 are the original supply and demand curves. D2 and D3 and S2 and S3 are possible new demand and supply curves. Starting from the initial equilibrium (point 1), which point on the graph is most likely to be the new equilibrium after the introduction of technological improvements in bicycle production and successful publicity campaigns by the government on the virtues of bicycling to work?
S1 and D1 are the original supply and demand curves. D2 and D3 and S2 and S3 are possible new demand and supply curves. Starting from the initial equilibrium (point 1), which point on the graph is most likely to be the new equilibrium after the introduction of technological improvements in bicycle production and successful publicity campaigns by the government on the virtues of bicycling to work?
A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D. 6
Which of the following is true if the production of a good gives rise to a positive externality?
A) The marginal social benefit from each level of output exceeds the consumers' willingness to pay. B) The marginal private benefit from production exceeds the marginal social benefit. C) The demand curve for the good shifts to the left in the presence of positive externalities. D) The demand curve for the good shifts to the right in the presence of positive externalities.
Describe at least three ways that global capital markets are different today from what they were like in the late nineteenth century
What will be an ideal response?
The text discusses unions in the context of the New Deal. It concludes that there was _____ in organized labor's relationship with government because _______
a. deterioration; Roosevelt's early speeches had created excessively high expectations. b. an improvement; labor gained the right to strike and organize free of employer interference. c. deterioration; organized labor was made subject to the same controls as big business. d. an improvement; military preparations reduced unemployment.