The money demand curve slopes:
a. downward because the cost of holding money decreases as the interest rate decreases
b. downward because the cost of holding money increases as the interest rate decreases.
c. upward because people demand more money as real GDP increases.
d. upward because people demand more money as real GDP decreases.
e. downward because people demand more money as the price level decreases.
a
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.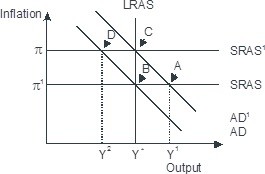
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary
Refer to Scenario 10.9. What is the profit maximizing level of output?
A) 0 B) 30 C) 45 D) 60 E) none of the above
The change in saving divided by the change in income is the
a. ratio of saving to income b. same as saving divided by income c. average propensity to save d. marginal propensity to consume e. marginal propensity to save
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as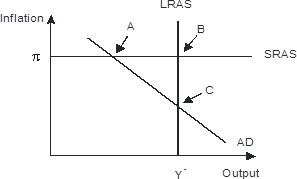
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward