The marginal product of labour is defined as
a) the amount of output produced by a given labour force
b) the minimum amount of workers required to produce a given level of output
c) the increase in productivity of the marginal worker if capital is increased
d) the amount of output one more worker could produce given other factors of production are fixed
e) the cost of employing another worker
d) the amount of output one more worker could produce given other factors of production are fixed
You might also like to view...
One reason the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping is because of the
A) interest rate effect. B) tariff effect. C) welfare effect. D) price effect.
Neuroeconomics is
A) the study of the activity of a human brain when the person makes economic decision. B) the study of how people behave when they face scarcity. C) the study of situations in which people act economically irrationally. D) the study of how people make decisions at the margin.
Refer to the data provided in Table 16.3 below to answer the following question(s).Table 16.3 shows the situation facing two firms, both of which are polluting. Assume that each firm emits 5 units of pollution.Table 16.3Firm AFirm AFirm AFirm BFirm BFirm BReduction of Pollution by Firm AMC of reducing pollution for Firm ATC of reducing pollution for Firm AReduction of Pollution by Firm BMC of reducing pollution for Firm BTC of reducing pollution for Firm B1$8 $81$16$16212202 24 40318383 32 72426644 401125361005 48160Refer to Table 16.3. Suppose the government wants to reduce the total amount of pollution from the current level of 10 to 4. To do this, the government caps each firm's emissions at 2 units and issues 2 permits to each firm. If firms are not allowed to trade
permits, what is the total cost of the pollution reduction? A. $60 B. $110 C. $116 D. $260
Refer to the figure. Assuming this market is representative of the economy as a whole, this economy:
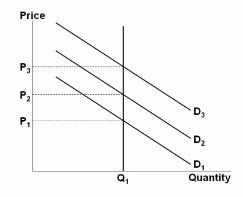
A. is highly susceptible to recessions and high unemployment.
B. faces regularly fluctuating output levels in response to demand shocks.
C. is capable of always producing at its optimal capacity.
D. can only lessen the impacts of business cycles through active government policy.