The preferred habitat theory of the term structure is closely related to the
A) expectations theory of the term structure.
B) segmented markets theory of the term structure.
C) liquidity premium theory of the term structure.
D) the inverted yield curve theory of the term structure.
C
You might also like to view...
What are the four main sources of comparative advantage? Briefly explain each source and provide examples
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is true? a. The private market provides too much of goods that generate external benefits
b. In the case of external benefits, if we could add the benefits that are derived by non-paying consumers, the supply curve would shift to the right, increasing output. c. In the case of external benefits, a tax equal to external benefits would result in an efficient level of output. d. In the case of public goods, when people act as free-riders, some goods having benefits greater than costs will not be produced.
When there are positive externalities in the consumption of a good:
a. marginal social benefit exceeds marginal private benefit. b. the marginal social benefit curve lies below the private market demand curve. c. the socially optimal level of output exceeds the private market equilibrium quantity. d. public policy aims to lower the level of output below the private optimum.
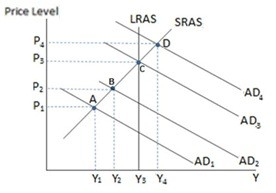 If the economy in the graph shown is at point D, and the government wished to bring the economy back to its long-run equilibrium, it might:
If the economy in the graph shown is at point D, and the government wished to bring the economy back to its long-run equilibrium, it might:
A. increase corporate income taxes. B. increase government spending. C. decrease income taxes. D. All of these would bring the economy back to potential GDP.