Austenitic stainless steel is _________corrosion resistant than ferritic stainless steel.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
more
You might also like to view...
If you toss a ball straight upward at 40 m/s, with no air resistance it returns to you at a speed of
A) zero. B) 10 m/s. C) 40 m/s. D) more than 40 m/s.
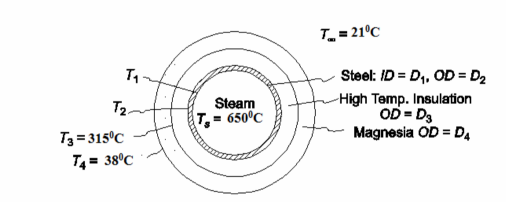
A standard 4 10 cm steel pipe (ID = 10.066 cm., OD = 11.25 cm) carries superheated steam at 650°C in an enclosed space where a fire hazard exists, limiting the outer surface temperature to 38°C. To minimize the insulation cost, two materials are to be used; first a high temperature (relatively expensive) insulation is to be applied to the pipe and then magnesia (a less expensive material) on the outside. The maximum temperature of the magnesia is to be 315°C. The following constants are known.

(a) Specify the thickness for each insulating material.
(b) Calculate the overall heat transfer coefficient based on the pipe OD.
(c) What fraction of the total resistance is due to (1) steam-side resistance, (2) steel pipe
resistance, (3) insulation (combination of the two), and (4) outside resistance?
(d) How much heat is transferred per hour, per foot length of pipe?
GIVEN
• Steam filled steel pipe with two layers of insulation
• Pipe inside diameter (Di) = 10.066 cm=0.10066 m
• Pipe outside diameter (Do) = 11.25 cm=0.1125 m
• Superheated steam temperature (Ts) = 650°C
• Maximum outer surface temperature (Tso) = 38°C
• Maximum temperature of the Magnesia (Tm) = 315°C
• Thermal conductivities
? High-temperature insulation (kh) = 0.1 W/(m K)
? Magnesia (km) = 0.076 W/(m K)
? Steel (ks) = 43 W/(m K)
• Heat transfer coefficients
? Steam side ( ci h ) = 500 W/(m2 K)
? Outside ( co h ) = 11 W/(m2 K)
• Ambient temperature (Ta) = 21°C FIND
(a) Thickness for each insulation material
(b) Overall heat transfer coefficient based on the pipe OD (c) Fraction of the total resistance due to
? Steam-side resistance
? Steel pipe resistance
? Insulation
? Outside resistance (d) The rate of heat transfer per unit length of pipe (q/L) ASSUMPTIONS
• The system is in steady state
• Constant thermal conductivities
• Contact resistance is negligible
SKETCH
A body is oscillating up and down at the end of a spring. Let's consider when the body is at the top of its up-and-down motion.The acceleration
a. is zero. b. has its largest magnitude. c. points up. d. points down.
A magnetic field of 2.00 T is applied to a bubble chamber to make the tracks of protons and other charged particles identifiable by the radius of the circles they move in. If a high-energy proton moves along an arc of a 3.30-m circle, what is the momentum of the proton? [q = 1.60 × 10^?19 C, m = 1.67 × 10^?27 kg]