The Federal Reserve Bank of New York
A) executes open market operations.
B) sets reserve requirements.
C) establishes the prime rate.
D) establishes the three-month Treasury bill rate.
A
You might also like to view...
Consider an income tax and a head tax, the sizes of which have been set so that the government collects the same amount of money under each tax. Which tax does the consumer prefer?
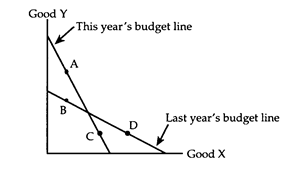
a. The consumer is indifferent between the two taxes, since he pays the same amount of money under each tax.
b. The consumer prefers the head tax, because it does not lower the relative wage as does the income tax.
c. The consumer prefers the income tax, because it can be avoided by increasing the amount of leisure time consumed.
d. The consumer may prefer either tax, depending on whether the income tax increases or decreases the number of hours of work at the optimum.
If a macroeconomic model consists of upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply and downward-sloping aggregate demand, can it possibly generate a constant real GDP with no business cycles over time?
A) No, only a vertical short-run aggregate supply curve can produce that result. B) No, only a horizontal short-run aggregate supply curve can produce that result. C) Yes, but the short-run aggregate supply curve must never shift. D) Yes, if the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves shift in perfect unison.
Which of the following is not an example of input growth that is a potential source of economic growth
a. immigration b. growth of the capital stock c. development of new technologies that reduce energy use. d. greater investment in workers' skills e. All of these are examples of input growth
In the United States during the 1930s:
A. government spending and taxes both increased, resulting in zero net fiscal expansion. B. government spending and taxes both decreased, resulting in a net fiscal contraction. C. government spending increased and taxes decreased, resulting in a fiscal expansion. D. government spending decreased and taxes increased, resulting in a fiscal contraction.