Which of the following is NOT an asset of the Federal Reserve?
A) currency
B) government securities
C) mortgage-backed securities
D) None of the above are correct because they are all assets of the Federal Reserve.
A
You might also like to view...
If marginal cost is constant, what happens to a market if it alters from perfect competition to monopoly without any change in the position of the market demand curve or any variation in costs?
A) Consumer surplus increases, and the previously existing deadweight loss decreases. B) Consumer surplus increases, and the previously existing deadweight loss increases. C) Consumer surplus is eliminated, and an equal-sized deadweight loss is created. D) Consumer surplus decreases in size, and a deadweight loss is created.
Which of the following statements is true?
a. Competitive markets result in the socially efficient price and quantity when externalities exist. b. Command-and-control regulations set an environmental goal and dictate how the goal will be achieved. c. Economists prefer command-and-control regulations to incentive-based pollution programs. d. An effluent tax is a tax imposed on rich people.
Aggregate demand and supply curves have been widely used to analyze the performance of the macroeconomy. Figure 5-3 shows four diagrams that represent different changes in the macroeconomy. Choose the diagram that best represents the situations described in the following questions.Figure 5-3
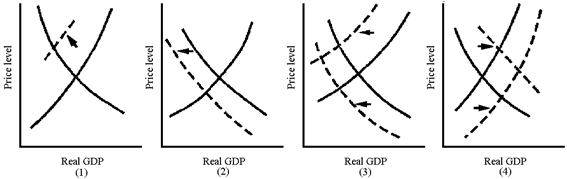
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
Assuming that firms maximize profits, how will the price and output policy of an unregulated monopolist compare with ideal market efficiency?
a. The output of the monopolist will be too large and the price too high. b. The output of the monopolist will be too large and the price too low. c. The output of the monopolist will be too small and the price too high. d. The output of the monopolist will be too small and the price too low.