Ethan enjoys buying books and going to the movies. He has income of $150 to spend on these two goods each month. The price of a book is $15 and the price of going to the movies is also $15. He currently consumes four books and six movies a month. If the price of a book increases to $20, then:
A. the substitution and income effects would both predict Ethan would consume more of both goods.
B. the substitution and income effects would both predict Ethan would consume less of both goods.
C. the substitution effect would predict Ethan would consume more books and less movies, and the income effect would predict he would consume less of both.
D. the substitution effect would predict Ethan would consume less books and more movies and the income effect would predict he would consume less of both.
D. the substitution effect would predict Ethan would consume less books and more movies and the income effect would predict he would consume less of both.
You might also like to view...
If Country A opens up their corn market to trade with the rest of the world and the global price of corn is lower than the equilibrium price of corn in Country A, then Country A will ________ corn, which will ________ consumer surplus, ________
producer surplus, and ________ total surplus. A) import; increase; decrease; increase B) import; decrease; increase; increase C) export; increase; decrease; increase D) export; decrease; increase; increase E) export; decrease; increase; decrease
What are the problems that arise when a commodity is used as money?
What will be an ideal response?
The most direct effect of an increase in the growth rate of average labor productivity would be an increase in
A) the inflation rate. B) the unemployment rate. C) the long-run economic growth rate. D) imported goods.
Figure 11-8
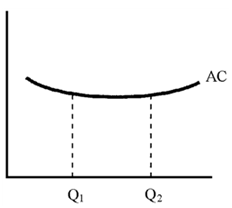
A. constant returns to scale . B. increasing returns to scale. C. decreasing returns to scale. D. externalities.