Ras is a GTP-binding protein involved in cell proliferation (division). In its active form, with GTP bound, Ras activates cell signaling pathways that promote cell division. Mutations in the gene that encodes Ras can lead to cancer. How might mutations in the gene encoding Ras lead to the uncontrolled proliferation characteristic of cancer cells?
A.) they increase the rate at which Ras hydrolyzes GTP
B.) they prevent Ras from being made
C.) they decrease the rate at which Ras hydrolyzes GTP
D.) they decrease the protein's affinity for GTP
E.) they increase the protein's affinity for GDP
Ans: C.) they decrease the rate at which Ras hydrolyzes GTP
You might also like to view...
Phylogenetic trees constructed from evidence from molecular systematics are based on similarities in _____
A) morphology B) the pattern of embryological development C) biochemical pathways D) mutations to homologous genes
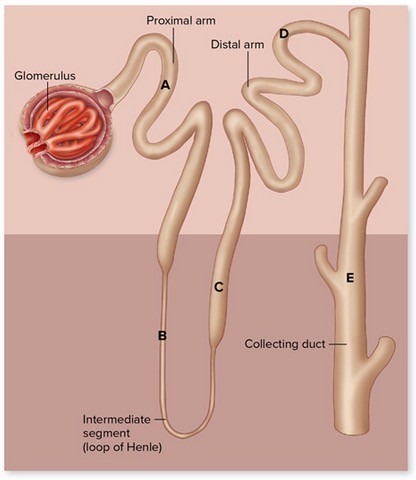 According to the above figure, which letter corresponds to the lowest tubular fluid osmolarity under normal conditions?
According to the above figure, which letter corresponds to the lowest tubular fluid osmolarity under normal conditions?
A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E
A(n) ________ is a large mass of inflammation and accumulated pus under the surface of an area of thick skin
A) carbuncle B) furuncle C) erysipelas D) mycetoma E) pox
Describe the difference between homologous and analogous structures in organisms, and give an example of each
What will be an ideal response?