You want to insert an aluminum rod, which at 20°C has a radius of 1.00020 cm into a copper tube which has a radius of 1.00010 cm at the same temperature
You decide to put both of them in the refrigerator. At what temperature will the rod just fit if both are cooled to the same temperature? The coefficient of thermal expansion for aluminum is 2.4 × 10-5K-1, and that of copper is 1.7 × 10-5K-1.
A)
7.8°C
B)
6.3°C
C)
9.2°C
D)
14.7°C
E)
5.7°C
E
You might also like to view...
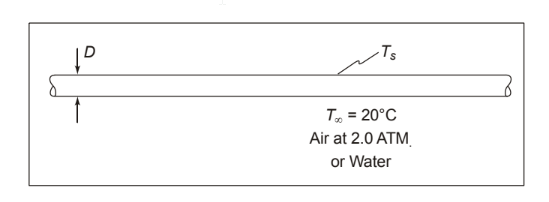
Compare the rate of condensate flow from the pipe in Problem 8.28 (air pressure = 200 kPa) with that for a 3.89-cm-OD pipe and 200 kPa air pressure. What is the rate of condensate flow if the 2 cm pipe is submerged in a 20°C constant-temperature water bath?
GIVEN
• A long horizontal copper pipe carrying saturated steam within an environmental testing chamber or a water bath
• Steam pressure = 120 kPa
• Ambient pressure (P) = 2 atm
• Ambient air or water temperature (T?) = 20°C
FIND
Rate of condensate flow for
(a) Diameter (D) = 3.89 cm = 0.0389 m Fluid is air at 2.0 atm
(b) Diameter (D) = 2 cm = 0.02 m Fluid is water at T? = 20°C
ASSUMPTIONS
• Pressure change has no effect on absolute viscosity, thermal conductivity, or specific heat of the air
• Air is still
• Convective thermal resistance on the inside of the pipe is negligible
• Thermal resistance of the copper pipe is negligible
• The air behaves as an ideal gas
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
For saturated steam at 0.12 MPa, the heat of vaporization (hfg) = 2238 kJ/kg, and the temperature (Ts) = 105°C.
for dry air at the mean temperature of 62.5°C and one atmosphere
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00298 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0281 W/(m K)
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 at P = 2.0 Atm,
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 9.83 × 10–6 Ns/m2
What is the primary way in which stars with masses similar to the Sun ultimately return some of their material to the interstellar medium?
A) by exploding as white dwarf supernovae B) through jets they may have during the protostar stage C) through planetary nebulae D) through the winds they have during their main-sequence lives E) Stars with masses similar to the Sun do not recycle any material back into the interstellar medium.
The energy released per reaction is smaller for fusion reactions than for the typical fission reactions. Yet fusion produces more energy per pound of fuel than fission of elements because
A. the daughter nuclei produced by fission each have excess kinetic energy. B. the fusion fuel consists of very light elements. C. fusion occurs in the sun.
The inertia of a body is directly related to its
a) force. b) mass. c) velocity. d) volume.