"For countries with fixed exchange rates, payments deficits would be self-correcting if only governments would stop doing their darnedest to prevent correction." Comment, and include how counterbalancing monetary policy (sterilization) can prevent self-adjustment from occurring.
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE: Under a payments deficit situation, the central bank would have to intervene by selling foreign currency and buying domestic currency in the foreign exchange market, to defend the fixed exchange rate. This would have a tendency to shrink the domestic money supply. Without counterbalancing policy (sterilization), the shrinking money supply would bid up domestic interest rates. The rise in interest rates decreases gross domestic product (GDP) and imports, so the current account improves. The rise in interest rates draws inflows of foreign capital (or reduces capital outflows), so the financial account improves. For both of these reasons, the payments deficit decreases, moving toward achieving external balance. However, the central bank could sterilize the effects of intervention, for instance, by buying domestic government bonds from the public. This would prevent the money supply from decreasing. If the money supply does not decrease, then domestic interest rates will not rise, and the adjustments of the current account and financial account will not happen.
You might also like to view...
The above figure illustrates the market for electric power that is served by the one utility in Alberta, Canada
a. If the government did not regulate this utility, what would be the price of a kilowatt hour in this region and how much power would be generated? b. If the government regulates the utility and chooses an average cost pricing rule, what would be the price of a kilowatt hour and how much power would be generated? c. If the government regulates the utility and chooses a marginal cost pricing rule, what would be the price of a kilowatt hour and how much power would be generated?
If the money multiplier is 3.5, a $10 billion increase in the monetary base
A) increases the quantity of money by $35 billion. B) increases the quantity of money by $2.86 billion. C) increases the quantity of money by $3.5 billion. D) increases the quantity of money by $10 billion.
Which of the following economic perspectives for decision making is a statement that describes the world as it is?
a. Positive statement b. Normative statement c. Cognitive statement d. Reflective statement
Figure 7-4
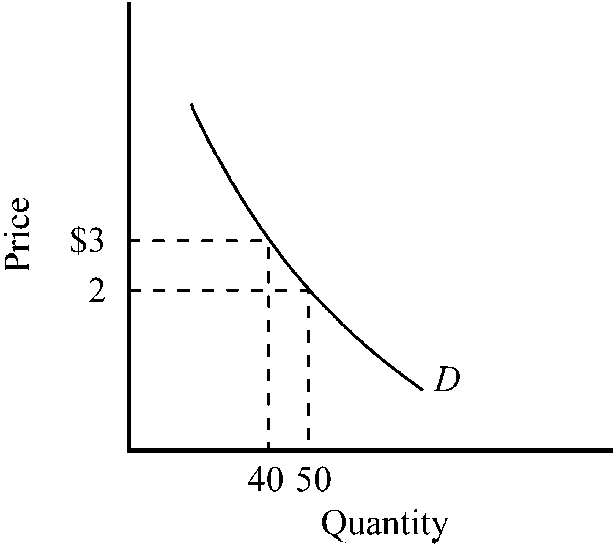
Which of the following is true for the demand curve depicted in ?
a.
An increase in price from $2 to $3 will reduce total expenditures on the product.
b.
In the $2 to $3 range, the price elasticity of the demand curve is approximately unitary.
c.
At a price of $2, the price elasticity of the demand curve equals approximately -2.5.
d.
In the $2 to $3 range, the demand curve is inelastic.