Suppose you cannot buy information that completely removes the uncertainty from a business decision that you face, but you could buy information that reduces the degree of uncertainty
Based on the discussion in this chapter, the value of this partial information could be determined as the: A) expected outcome under complete certainty minus the expected outcome under the partial information case.
B) expected outcome under the partially uncertain case minus the expected outcome under the completely uncertain case.
C) utility of the partially certain case minus the utility of the completely certain case.
D) We cannot determine the value of information under partial certainty.
B
You might also like to view...
Countries that engage in trade will tend to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have ________ and will ________ these goods and services
A) a comparative advantage; export B) a comparative advantage; import C) an absolute advantage; import D) an absolute advantage; export
Which of the following is true?
a. GDP is a "flow" concept. b. The purchase prices of both intermediate goods and final goods are included in GDP. c. GDP measures economic welfare. d. GDP is a measure of changes in the general level of prices.
Since the 1950s, total expenditures in the United States nearly tripled to about 60 percent of GDP
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the graph below, which shows the market for bicycles. S1 and D1 are the original supply and demand curves. D2 and D3 and S2 and S3 are possible new demand and supply curves. Starting from the initial equilibrium (point 1), what point on the
graph is most likely to be the new equilibrium after a sharp increase in traffic accidents involving cyclists, and the payment of subsidies to bicycle producers?
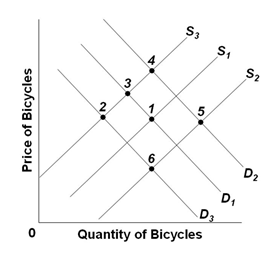
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6