A physics professor places a soda pop can on the table and asks a student to identify the forces acting upon the can and the directions of each force. The two forces acting on the soda pop can are
A. the weight force upward and normal force from the table upward.
B. the weight force downward and normal force from the table upward.
C. the weight force upward and normal force from the table downward.
D. the weight force downward and normal force from the table downward.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
A 1.5-kg object has a velocity of 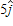
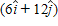
A. 3.8 N B. 3.2 N C. 2.8 N D. 4.3 N E. 4.6 N
What is the evidence that suggests planetary systems are common in the universe?
What will be an ideal response?
Molar Specific Heats: For an ideal gas,
A. 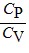 = 1 for all ideal gases.
= 1 for all ideal gases.
B. 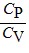 < 1 for all monatomic and diatomic gases.
< 1 for all monatomic and diatomic gases.
C. 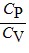 > 1 for all monatomic and diatomic gases.
> 1 for all monatomic and diatomic gases.
D. 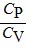 < 1 only for a monatomic gas.
< 1 only for a monatomic gas.
E. 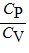 < 1 only for a diatomic gas.
< 1 only for a diatomic gas.
Suppose you want to set up a simple pendulum with a period of 0.250 s
(a) What length is required if g = 9.80 m/s2 on Earth? (b) What length would be required on the moon assuming g is 6 (assume exact) times LESS than on Earth?