Union membership will be more attractive from the worker's viewpoint if
a. the demand for the union labor is highly inelastic.
b. the supply of union labor is highly elastic.
c. only a few of the firms in the industry are unionized.
d. the membership dues charged by the union are extremely high.
A
You might also like to view...
As demonstrated by the labor supply schedule, the quantity of labor supplied depends on
A) workers' productivity. B) the value of the dollar. C) the nominal wage. D) the amount of labor that firms want to hire. E) the real wage.
Great Benefit is a health insurance company with two types of customers: healthy persons and sickly persons. A healthy person has 1-to-5 odds of getting ill, and a sickly person has 1-to-1 odds of getting ill. However, the insurance company cannot distinguish between healthy and sickly persons. Brett is a risk-averse person who purchases health insurance from Great Benefit. Without insurance, Brett's income will be $8,000 if he remains healthy and $2,000 if he becomes ill. Brett's situation is diagrammed below.
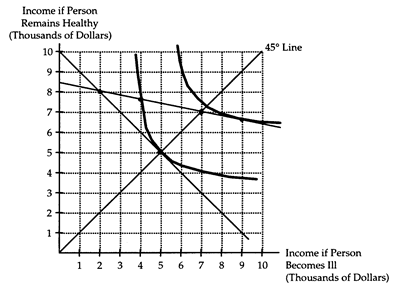
(i) Is Brett a healthy person or a sickly person? How can you tell?
(ii) Suppose Great Benefit offers two policies-one at fair odds for healthy persons and one at fair odds for sickly persons-that can be purchased in unlimited quantities. What type of policy and how much insurance will Brett choose to purchase?
(iii) What type of information problem does the insurance company face? What limit should the insurance company place on insurance at "healthy" odds to deal with this problem?
Suppose a monopolist is able to charge each customer a price equal to that customer's willingness-to-pay for the product. Then the monopolist is engaging in
a. marginal cost pricing. b. arbitrage pricing. c. voodoo economics. d. perfect price discrimination.
Expected economic profit per unit is equal to:
A. expected price. B. expected average total cost. C. the difference between expected total revenue and expected total cost. D. the difference between expected price and expected average total cost.