Which of the following is not a property of standard indifference curves in a leisure-consumption model?
A. Higher indifference curves (to the northeast) indicate higher levels of utility.
B. Indifference curves tend to be downward sloping.
C. Indifference curves intersect one another.
D. Indifference curves tend to be convex to the origin.
E. There is an indifference curve passing through every leisure-consumption bundle.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 2-20. Does either Japan or Thailand have an absolute advantage and if so, in what product?
A) Thailand has an absolute advantage in rice. B) Japan has an absolute advantage in rice. C) Japan has an absolute advantage in wristwatches. D) Thailand has an absolute advantage in both products.
Given the assumptions of the classical model
A) the economy will often experience recessions and expansions. B) expansion will be the normal condition, but recessions will often be severe and require government intervention. C) the macroeconomy is erratic, and problems will often be increased over time. D) the market is a self-correcting mechanism.
A technological advance that increases labor productivity will
a. lower wages. b. decrease the demand for labor as fewer workers are needed. c. decrease the supply of labor as fewer workers are needed. d. increase the demand for labor as MP rises. e. decrease the demand for labor as MP falls.
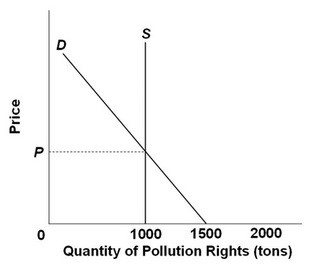 Refer to the above diagram illustrating a market for pollution rights in which government has fixed the supply of rights at 1,000 tons. If the demand for pollution rights were to increase as a result of economic growth, the:
Refer to the above diagram illustrating a market for pollution rights in which government has fixed the supply of rights at 1,000 tons. If the demand for pollution rights were to increase as a result of economic growth, the:
A. volume of pollutants discharged would increase. B. supply curve would shift to the right. C. price of pollution rights would increase. D. demand curve would shift to the left.