How do we know that pulsars must be very small in size (radius)?
A) We have measured their radii directly in high-resolution telescope images.
B) Their small sizes are inferred from careful study of their spectra.
C) Some spin so rapidly that if they were larger in size, their surfaces would be moving faster than the speed of light.
D) Only very small objects can beam radiation into space.
E) This is only a theory that has not yet been confirmed by observations.
C) Some spin so rapidly that if they were larger in size, their surfaces would be moving faster than the speed of light.
You might also like to view...
Two kilograms of molten copper at 1083ºC are dropped into water at 40ºC. Determine the freezing time for complete solidification of the copper. Assume lumped heat capacity and that the heat of fusion of copper is 204.7 kJ/kg and the convective heat transfer coefficient have is 120 W/m2?K. Hint: Use Equation 10-66 for freezing instead of melting.
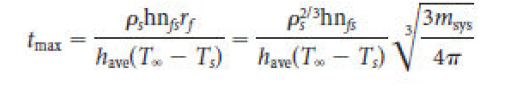
A particle is being accelerated through space by a 10-N force. Suddenly the particle encounters a second force of 10 N in the opposite direction. The particle with both forces acting
A) is brought to a rapid halt. B) decelerates gradually to a halt. C) continues at the same speed it had before encountering the second force. D) theoretically tends to accelerate toward the speed of light. E) none of the above
Latent Heats: A 45.0-kg sample of ice is at 0.00°C. How much heat is needed to melt it? For water LF = 334,000 J/kg and LV = 2.256 × 106 J/kg.
A. 1.50 × 104 kJ B. 4.10 × 106 kJ C. 0.00 kJ D. 1.02 × 105 kJ
The proton-proton chain
a. combines two hydrogen nuclei to produce a single helium nucleus and energy. b. splits a helium nucleus to produce 4 hydrogen nuclei and energy. c. is the mechanism that increases the temperature between the photosphere and corona of the sun. d. is the interactions between protons in Earth's atmosphere that produces auroras. e. produces energy in the core of the sun in the form of gamma-rays, positrons, and neutrinos.