Consider a market with just one firm. The demand in the market is p = 18 – Q and the firm has a linear cost function C(Q) = 2Q
a. How much output will this firm produce. What will be the profit and consumers surplus?
b. Suppose a second firm with the same cost function enters the market and the two firms compete in a Cournot style (simultaneous output choice). What will be the equilibrium price and quantity in the market? What is the total market profit and CS?
a. A monopolist will produce to maximize profits given by:
= (18 – Q)Q - 2Q
The derivative w.r.t Q:
- 2Q - 2 = 0
So Q = 8
The price is then $10. The profit is $10(8 ) - 2(8 ) = 64. The Consumer surplus is (18 - 10 )(8 )/2 = 32.
b. Each firm will maximize profit by:
π = (18 - Q - Qo)Q - 2Q
where Q0 is the output of the other firm. The derivative is:
18 - Qo - 2Q - 2 = 0
The best response is:
Q = 8 - Qo/2
Solving both best response functions simultaneously:
Q = 8 - (8 - Q/2 )/2
Q = 16/3 = 5.33. The total market quantity is then 10.66. The price is 18 - 10.66 = 7.34. The profit for each firm is:
5.33 (7.34 ) - 5.33(2 ) = 28.41
The total market profit is then 56.82
The consumer surplus is (18 - 7.34 )(10.66 )/2 = 56.87
You might also like to view...
Under the social interest theory of regulation, the goal of regulating natural monopolies is
A) to provide a larger, though not maximum, profit for the firms. B) to use average cost pricing. C) to provide an outcome similar to the competitive outcome. D) to provide a the maximum profit for the firms. E) None of the above answers is correct.
Refer to the above table. If opportunity costs are constant, then the opportunity cost of producing good B in country X is ________, and the opportunity cost of producing good B in country Y is ________
A) 1 unit of A; 2 units of A B) 1 unit of A; 0.5 unit of A C) 1 unit of B; 2 units of A D) 1 unit of A; 0.5 unit of B
Suppose the equilibrium price in a perfectly competitive industry is $100 and a firm in the industry charges $112 . Which of the following will happen?
a. The firm will not sell any of its output. b. The firm will sell more output than its competitors. c. The firm's profits will increase. d. The firm's revenue will increase. e. The firm will gradually take over the entire industry.
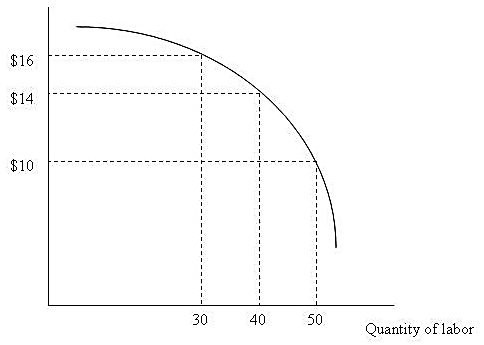
 Figure 10.1 depicts a firm's marginal revenue product curve. If the product price decreases, the marginal revenue product curve:
Figure 10.1 depicts a firm's marginal revenue product curve. If the product price decreases, the marginal revenue product curve:
A. shifts downward. B. shifts upward. C. remains the same. D. None of these