Explain how the threat of a leveraged buyout or a takeover can actually address the problem of moral hazard.
What will be an ideal response?
The potential for moral hazard exists in most corporations because the managers or officers of the corporation are often not the owners; this is called the principal-agent problem. The managers may not always act in the best interest of the owners. For example, the owners may prefer a higher return that calls for a greater risk to be taken. The managers (preferring to keep their jobs) may shun the additional risk, preferring the job security over a higher return for the owners. The threat that the company can be and likely may be purchased by others if it is under performing can actually motivate the managers to seek a higher return.
You might also like to view...
Outline the various actions the government sector could take to promote growth
What will be an ideal response?
A basket of goods cost $100 in the U.S. and £65 in the United Kingdom. If purchasing power parity holds, what is the dollar-pound exchange rate?
What will be an ideal response?
The principle of voluntary exchange is based on the idea of:
A. making assumptions. B. isolating variables. C. thinking at the margin. D. rational self-interest.
Figure 7.5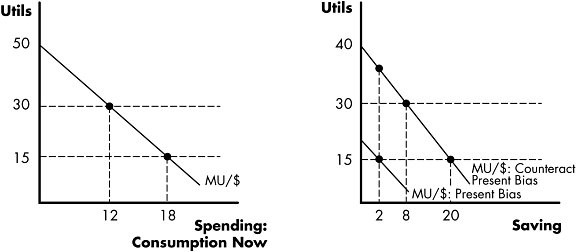 The consumer must decide how to split $20 between spending and saving.Refer to Figure 7.5. If the consumer uses cognition to offset present bias, he/she will maximize utility at a marginal utility per dollar of ________ utils for consumption and ________ utils for saving.
The consumer must decide how to split $20 between spending and saving.Refer to Figure 7.5. If the consumer uses cognition to offset present bias, he/she will maximize utility at a marginal utility per dollar of ________ utils for consumption and ________ utils for saving.
A. 15; 15 B. 15; 30 C. 30; 15 D. 30; 30