Theoretically, profit maximization occurs at P* and q* in the short run. However, empirical work suggests that oligopolists often actually charge P 1 . Which deterrence strategy best incorporates this action?
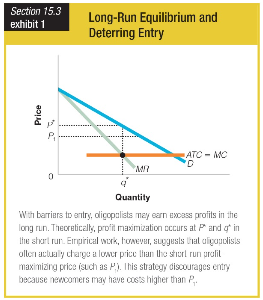
a. The oligopolist maintains P* until the threat of entry subsides, then lowers the price to
P 1 .
b. The oligopolist maintains P1 until the threat of entry subsides, then keeps the price at
P 1 .
c. After the threat of entry subsides, the oligopolist lowers the price below P 1 .
d. After the threat of entry subsides, the oligopolist raises the price to the profit-
maximizing price.
d. After the threat of entry subsides, the oligopolist raises the price to the profit-
maximizing price.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements would make a reasonable hypothesis to test?
A) Deflation is worse than inflation in any economy. B) An unemployment rate below 4% is bad for the economy. C) As tax rates increase, eventually tax revenues will decline. D) Higher real GDP per capita figures lead to happier citizens.
The equation representing the final demand approach to calculating GDP is
A. Y = C + I + X + IM. B. Y = C + I + G. C. Y = G + I + X ? IM. D. Y = C+ I + G + (X ? IM).
If GDP is too high relative to potential GDP, which of the following happens?
A. Inflation rises B. Unemployment rises C. A recession begins D. Deflation occurs
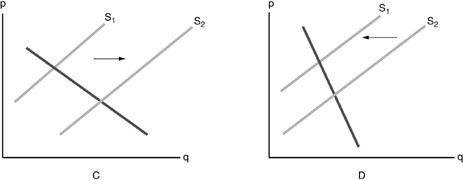 Refer to the above figure. Which diagram shows the effect on the market of cellphones when the demand for cellphones has increased?
Refer to the above figure. Which diagram shows the effect on the market of cellphones when the demand for cellphones has increased?
A. graph C B. graph D C. neither graph D. both graphs