Answer: d. quantity demanded stays the same whenever price changes.
In the case of perfectly inelastic demand,
a. the change in quantity demanded equals the change in price.
b. the percentage change in quantity demanded equals the percentage change in price.
c. infinitely-large changes in quantity demanded result from very small changes in the price.
d. quantity demanded stays the same whenever price changes.
You might also like to view...
The steeper the short-run aggregate supply curve, _____
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
The allocative function of price is to:
A. direct resources away from markets that are overcrowded and toward markets that are underserved. B. provide subsidies to low-income families so they can purchase essential goods and services. C. ensure that firms in perfectly competitive markets earn an economic profit. D. distribute scarce goods and services to those consumers who value them the most highly.
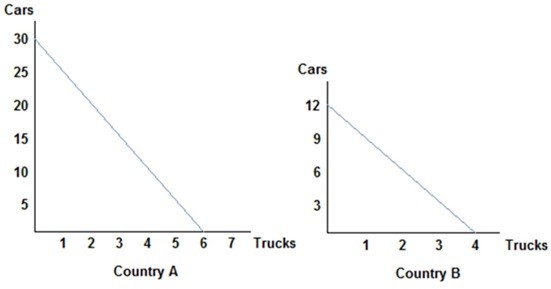 Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. The slope of Country A's production possibilities frontier:
Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. The slope of Country A's production possibilities frontier:
A. measures the trade-off that Country A face when deciding how to allocate resources. B. measures the opportunity cost of trucks in terms of cars. C. is constant because the opportunity cost remains constant. D. All of these statements are true.
The expected damage to innocent third parties per unit of the good produced is shown as the "external cost" in Figure 27.1. An unregulated competitive market for the product produces a quantity of Q* units, which sell for a price of P* per unit. If the competitive industry were producing the socially optimal quantity of this product, the market price of the product per unit would be 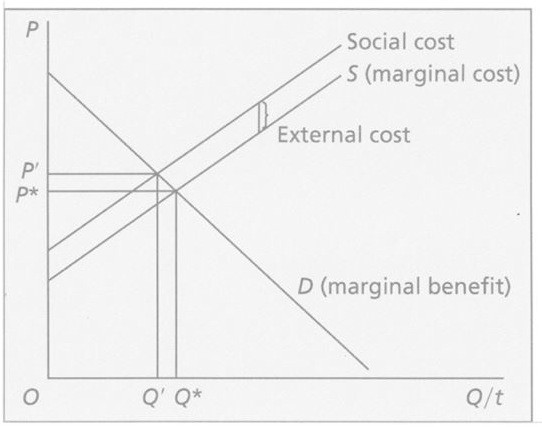
A. P?-P*. B. P?. C. P*. D. zero.