The main international repercussion of either a fiscal expansion or monetary contraction is to
a. raise interest rates and the exchange rate, thereby crowding out net exports.
b. raise interest rates and lower the exchange rate, thereby crowding in net exports.
c. lower interest rates and the exchange rate, thereby crowding in net exports.
d. lower interest rates and raise the exchange rate, thereby crowding out net exports.
a
You might also like to view...
Most people buy salt infrequently and in small quantities. Even a doubling of the price of salt is likely to result in a small decline in the quantity of salt demanded. Therefore
A) the price elasticity of demand for salt is greater than 1 (in absolute value). B) the demand for salt will be perfectly inelastic. C) salt is a normal good. D) the demand for salt is relatively inelastic.
Which of the following is true of the tax and transfer programs of the United States?
a. Tax-transfer programs persistently redistribute income from the rich to the poor. b. Social Security, the largest transfer program, redirects income toward the elderly, a group with above-average levels of both income and wealth. c. The bulk of agriculture subsidies go to large farmers with above-average incomes. d. Taxes generally take a larger share of the income of the poor than is true for those with higher incomes. e. Both b and c are true.
Suppose the demand and supply curves for good X are both linear. The demand price for the first unit of X is $28, and the supply price for the first unit of X is $6. If the equilibrium price for good X is $16 and the equilibrium quantity of X is 24,000 units, then total consumer surplus is ________, total producer surplus is ________, and total social surplus is ________.
A. $144,000; $672,000; $384,000 B. $144,000; $120,000; $264,000 C. $672,000; $144,000; $384,000 D. $28; $6; $16 E. $120,000; $144,000; $264,000
Refer to the graph shown. Expansionary fiscal policy shifts the aggregate demand curve from: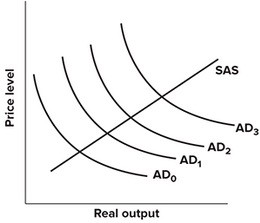
A. AD0 to AD2 whether or not crowding out occurs. B. AD0 to AD2 but then back to AD1 if crowding out occurs. C. AD0 to AD2 but then out to AD3 if crowding out occurs. D. AD2 to AD1 and then from AD1 to AD0 if crowding out occurs.