Suppose that a university decides to spend $1 million to upgrade personal computers and scientific equipment for faculty rather than spend $1 million to expand parking for students. This example illustrates:
A. distorted priorities.
B. opportunity costs.
C. increasing opportunity costs.
D. productive efficiency.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Caterpillar has spent $5 million to date on a new plant, and another $2 million is needed to complete the plant. When construction was started, it was projected that production at the new plant would add $12 million to Cat's profit, but new projections show the additional profit will be only $6 million. Assuming the incomplete plant is worthless, should Cat complete the new plant or abandon it?
a. Cat should complete the plant because it would create a net profit of $4 million. b. Cat should complete the plant because it would create a net profit of $1 million. c. Cat should abandon the plant because a $5 million loss is better than a $7 million loss. d. Cat should abandon the plant because it would create a net loss of $1 million..
Gross domestic product (GDP) is
a. the total value of all goods and services produced for the marketplace during a given period, within a nation's borders b. the total value of all final goods and services produced for the marketplace during a given period, by a nation's citizens and businesses, both within a nation's borders and abroad c. the total value of all final goods and services produced for the marketplace during a given period, within a nation's borders d. the total value of all goods and services produced for the marketplace during a given period, by a nation's citizens and businesses e. the total value of all goods, services and inputs produced for the marketplace during a given period, within a nation's borders
Refer to the graph shown.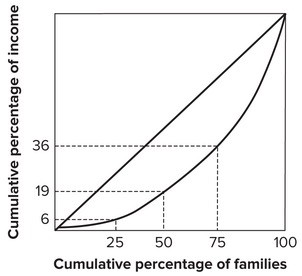 The poorest 50 percent of the families earn:
The poorest 50 percent of the families earn:
A. 19 percent of the income. B. 64 percent of the income. C. 6 percent of the income. D. 36 percent of the income.
Which of the following is FALSE?
A) At the end of the twentieth century, more and more traded goods and services incorporated specialized knowledge and unique ideas. B) Pharmaceuticals, computer hardware, telecommunications equipment, and other high technology products are valuable because of the innovation and research they incorporate. C) Developing countries usually strongly advocate the protection of intellectual property rights. D) The protection given to creators and innovators varied greatly internationally until standardization began with the signing of the TRIPs agreement.