Number 11. According to the figure, expansionary monetary policy will cause an economy that is initially at full-employment output to go from equilibrium ______ to equilibrium ______ in the short run.
a. A; C
b. A; B
c. A; D
d. C; B
b. A; B
You might also like to view...
The payoff matrix below shows the payoffs (in millions of dollars) for two firms, A and B, for two different strategies, investing in new capital or not investing in new capital. 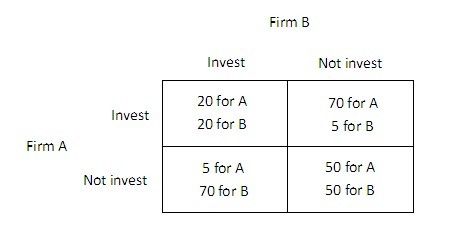 An industry spy from firm A comes to firm B and offers to pay B in exchange for B's certain and enforceable promise to not invest. What is the most that firm A will be willing to pay B to not invest?
An industry spy from firm A comes to firm B and offers to pay B in exchange for B's certain and enforceable promise to not invest. What is the most that firm A will be willing to pay B to not invest?
A. $35 million. B. $20 million. C. $30 million. D. $50 million.
Which of the following is an allowable deduction?
A. Unreimbursed medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of AGI B. State and local income and property taxes C. Interest on qualified education loans up to a certain limit D. All of the answer options are correct.
In order to smooth the influence of shocks throughout an economy, it is helpful for governments within a monetary union to have
A) ways to conduct fiscal transfers. B) seignorage. C) currency competition. D) monetary autonomy.
Empirical studies have found that the labor supply curves for most parts of the population are
A) backward bending. B) upward sloping. C) downward sloping. D) nearly vertical.