A favorable supply shock will shift short-run aggregate supply
a. left, making output rise.
b. left, making output fall.
c. right, making output rise.
d. right, making output fall.
c
You might also like to view...
Suppose the base reference period is 1982-1984. If your nominal wage rate is $8.00 per hour when the CPI is 180, what is your real wage rate in 1982-1984 dollars?
What will be an ideal response?
Assume that an inflationary gap must be closed by reducing aggregate expenditures. If consumers refuse to cut spending on consumption and producers won't cut demand for investment goods, the President:
a. can do nothing. b. must build more roads. c. must borrow from Wall Street. d. must increase Social Security expenditures. e. must cut government spending.
A decrease in the price of a particular good, with all other variables constant, causes
a. a shift to a different demand schedule with higher quantities demanded b. a shift to a different demand schedule with lower quantities demanded c. a movement along a given demand curve to a lower quantity demanded d. a movement along a given demand curve to a higher quantity demanded e. no movement along a given demand curve unless supply also changes
In this graph, what is different about equilibrium levels E1 and E3 compared to e2?
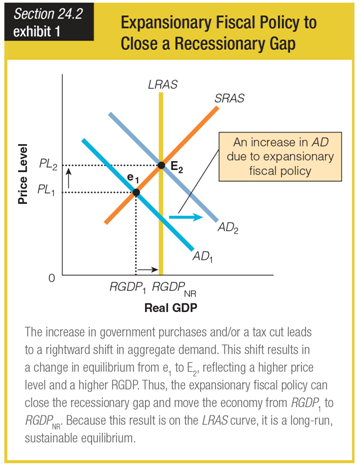
a. Price levels are higher at both E1 and E3 than at e2.
b. Price levels are lower at both E1 and E3 than at e2.
c. Level e2 is sustainable, whereas levels E1 and E3 are not.
d. Levels E1 and E3 are both sustainable, whereas e2 is not.