A decrease in the price of a particular good, with all other variables constant, causes
a. a shift to a different demand schedule with higher quantities demanded
b. a shift to a different demand schedule with lower quantities demanded
c. a movement along a given demand curve to a lower quantity demanded
d. a movement along a given demand curve to a higher quantity demanded
e. no movement along a given demand curve unless supply also changes
D
You might also like to view...
A chief purpose of long-term contracts is to improve agents'
A) information. B) incentives. C) control over principals. D) security.
According to the search model, we should expect greater price dispersion for a given good
a. if the good is a luxury b. if the good is inferior c. if there is much common knowledge about the good d. during a recession e. if a computerized search service is offered
Consider the production possibilities frontier displayed in the figure shown. A society should choose to produce:
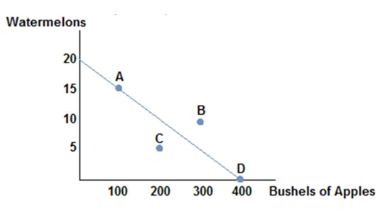
A. at point C because it is the safest.
B. at point B because it represents the most the society can produce.
C. at any point that produce some of each good.
D. at any point on the frontier rather than inside it.
Suppose the economy has been experiencing zero inflation and 5 percent unemployment for several years. The government decides to lower the unemployment by generating some inflation. Using a graph, show what the short-run effects would be and what would happen in the long run. What would the government have to do to keep the unemployment rate at 3 percent?
What will be an ideal response?