When an economy is in an economic boom, discretionary fiscal policy would call for _____________, and the automatic stabilizers would _____________.
A. lowering tax rates; lower tax revenues
B. lowering tax revenues; lower tax rates
C. increasing tax rates; increase tax revenues
D. increasing tax rates; lower tax revenues
C. increasing tax rates; increase tax revenues
You might also like to view...
Assuming the firm in the graph shown is producing Q1 and charging P3, it is likely showing the cost and revenue curves of a monopolistically competitive firm that is:
These are the cost and revenue curves associated with a firm.
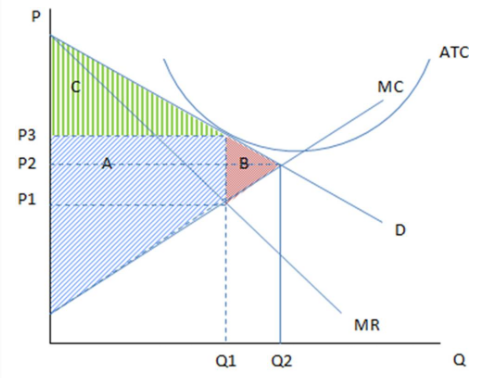
A. making positive economic profits.
B. earning negative economic profits.
C. in long-run equilibrium.
D. All of these statements are true.
If interest rates in Canada rise above those in the rest of the world, then
a. the demand for Canadian dollars decreases b. exports from Canada to other countries increases c. imports into Canada from other countries decreases d. it raises Canada's exchange rate and this may result in a deficit on Canada's current account e. the balance of payments becomes negative
Based on the graphs for an increase in aggregate demand and the Phillips curve, we can see that when inflation is high, ______.
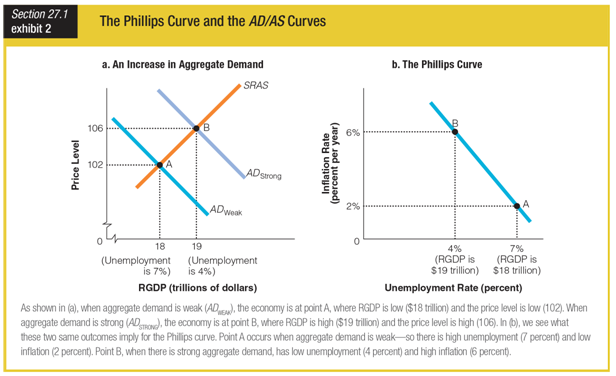
a. RGDP is low
b. unemployment is high
c. aggregate demand is weak
d. aggregate demand is strong
During the early 1980s, the U.S. economy experienced an increase in interest rates quoted on U.S. Treasury debt, business loans, and mortgages. At the same time the inflation rate gradually declined more than expected. What happened to ex ante versus ex post real interest rates during this period? Use the Fisher equation to support your answer.
What will be an ideal response?