A sudden increase in inflation, ceteris paribus,
A. Raises the CPI and reduces real income.
B. Raises the real income of lenders relative to borrowers.
C. Makes everyone worse off.
D. Reduces the nominal income of those who have constant real incomes.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the above table. Suppose the firm hires 4 workers and the price of the good sold is $4. The marginal factor cost of labor must be
A) $4. B) $150. C) $3080. D) $600.
If the shifts in AD that will result from policy changes are fully and accurately anticipated, an increase in government purchases or a decrease in taxes would result in which of the following in the short run?
a. a higher level of real output and a higher price level b. a higher level of real output but no change in the price level c. a higher price level and a reduced level of real output d. a higher price level but no change in real output
Jesse wants to maximize her net gains from working. She estimates that the 12th hour of work per week yields $10 of additional monetary and nonmonetary benefits, but involves $9 in additional costs. She should:
a. work for only 11 hours per week, since the 12th hour yields such a small net gain. b. work the 12th hour only if she can negotiate a higher wage for that hour. c. definitely work the 12th hour since doing so raises her net gain from working. d. work for only 11 hours since it doesn't make sense to undertake work that has positive costs associated with it
The figure below depicts the IS-LM-FE model with floating exchange rates.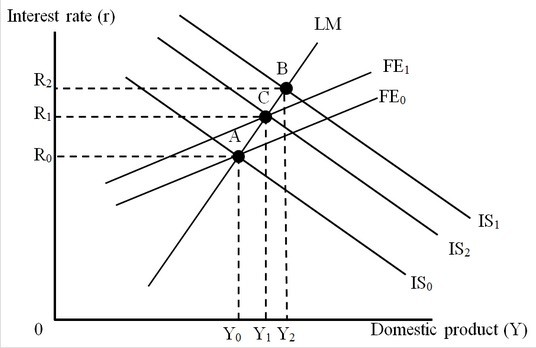 The move from Point A to Point B is caused by
The move from Point A to Point B is caused by
A. contractionary fiscal policy. B. expansionary monetary policy. C. expansionary fiscal policy. D. contractionary monetary policy.