Assuming a homogeneous product, the Bertrand equilibrium price is
A) independent of the number of firms.
B) independent of the firm's marginal costs.
C) equal to the Cournot equilibrium price.
D) equal to the monopoly price.
A
You might also like to view...
Refer to Exhibit 10-2. At M,
a. TP > TE. b. the relationship between TP and TE cannot be determined. c. TE > TP. d. TP = TE.
Hotelling's model has been used to describe differentiation in the political "market." Suppose that 100 voters are evenly distributed between the extreme left and the extreme right on the political spectrum, and that all voters vote, and they always vote for the candidate closest to them on this spectrum. The numbers on this spectrum represent the number of voters lying to the left of the number. So, at the midpoint, fifty voters lie to the left and fifty to the right.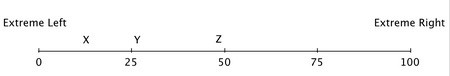 To an economic naturalist, this model helps explain why political candidates:
To an economic naturalist, this model helps explain why political candidates:
A. move toward more centrist positions during campaign season. B. work to bring federally funded projects to their home districts. C. take more extreme positions than are held by the general population. D. are loyal to their political parties.
Maximum Feasible Hourly Production Rates of EitherComputers or Bicycles Using All Available ResourcesProductUnited StatesChinaComputers83Bicycles26 Refer to the above table. If opportunity costs are constant and the two countries trade
A. the United States should specialize in bicycles and China in computers. B. the United States should specialize in both bicycles and computers, and China should specialize in neither. C. the United States should specialize in computers and China in bicycles. D. there will be no trade because they are so different.
For you to be considered not in the labor force, you can be
A. a full-time volunteer. B. a full-time retiree. C. a full-time student. D. any of the above.