Country A produces 10 chairs and 6 tables using its resources. Country B produces 12 chairs and 18 tables. Determine the comparative advantage and the absolute advantage that both countries enjoy
What will be an ideal response?
The opportunity costs of producing each good in the two countries are shown below.
Opportunity cost of producing a chair in Country A = 0.6 tables.
Opportunity cost of producing a chair in Country B = 1.5 tables.
Hence, Country A has a comparative advantage in producing chairs.
Opportunity cost of producing a table in Country A = 1.67 chairs.
Opportunity cost of producing a table in Country B = 0.67 chairs.
Hence, Country B has a comparative advantage in the production of tables.
Because the opportunity cost of producing tables is less in Country B, Country B has a comparative advantage in the production of tables. On the other hand, Country A has a comparative advantage in producing chairs.
Country B can produce more of both the goods than Country A; therefore, it enjoys an absolute advantage in the production of both goods.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is an example of a fiscal stimulus?
A) decrease in transfer payments B) decrease in taxes C) decrease in government expenditure on goods and services D) increase in taxes E) none of the above
Suppose a wallet firm has been dumping its wastes into the local river. The government finds out and insists that the firm pay for the cost of the river cleanup. As a result, we can expect:
a. more wallets to be produced at a lower price. b. more wallets to be produced at a higher price. c. fewer wallets to be produced at a lower price. d. fewer wallets to be produced at a higher price. e. the same number of wallets to be produced at a higher price.
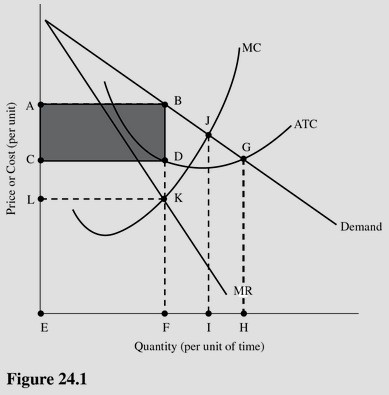 In Figure 24.1, total profit is represented by the area
In Figure 24.1, total profit is represented by the area
A. CDFE. B. ABGHE. C. ABFE. D. ABDC.
Economic analysis is used
A. only by instructors and students in economics to understand the world. B. only by policy makers to make policy decisions. C. only by business people to raise profits. D. in decision making.