Which of the following explains the spread of financial crises from one country to another?
A. Moral hazard
B. Global contagion
C. Butterfly trade
D. The Doppler effect
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
An example of an "investment" financial intermediary is
A) an insurance company. B) a private pension fund. C) a credit union. D) a mutual fund.
Some firms provide stock options to managers as an incentive to work hard and increase the value of the firm. A typical option contract gives the manager the right to buy the firm's stock at a set price (known as the exercise price)
If the firm's stock value increases and moves above the exercise price, then the manager's option becomes more valuable. What is the potential problem with this incentive scheme? A) The incentive does not include a performance benchmark, so it cannot be optimal. B) There is a dynamic incentive problem --- the manager may focus too much on the firm's short-run stock value and not on actions that are in the best interest of the firm for the long run. C) The incentive value depends on the firm's stock value, which cannot be influenced by the amount of work or effort exerted by the manager. D) There are no problems with this incentive scheme.
In the above figure, if this natural monopolist were forced to use marginal cost pricing, it would produce
A) at Q1 output rate. B) at Q2 output rate. C) at Q3 output rate. D) past the Q3 output rate.
Refer to Figure 1. The figure represents a circular-flow diagram. Boxes C and D represent
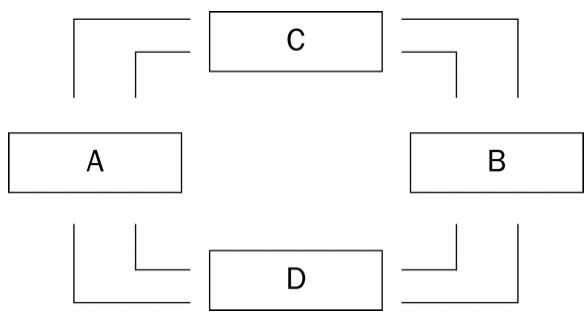
a. households and government.
b. firms and government.
c. the markets for goods and services and the financial markets.
d. None of the above are correct.