Why did the USSR collapse and China succeed? Explain
What will be an ideal response?
In contrast to the Russian experience, the Chinese economy did not decline at all during its transition from communism to capitalism. The proponents of rapid reform see China as a special case. First, central planning was less extensive in China, with the result that its economy was less distorted and less overconcentrated on heavy industry. Second, and most importantly, China's economy is much more agricultural. In 1978, when China began its reforms, 71 percent of the labor force was in agriculture. The figure for Russia in 1990 at the beginning of its transition was 13 percent. China's heavier concentration in agriculture gives it a large rural labor force with very low productivity. If these workers leave the countryside, the resulting loss of output is small, while the offsetting productivity gains from employment in urban and village industrial enterprises are significant. Hence, China can move labor from agriculture into the new enterprises, but Russia had to take labor out of heavy industry to staff the new enterprises.
You might also like to view...
If real GDP is greater than nominal GDP then the GDP price index
A) is greater than 100. B) is less than 100. C) is equal to 100. D) is either equal to or greater than 100. E) None of the above answers is correct because we need to choose a new base year.
The U.S. income tax
a. discourages saving. b. encourages saving. c. has no effect on saving. d. will reduce the administrative burden of taxation.
The basic conservative solution to welfare dependency is _____________________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
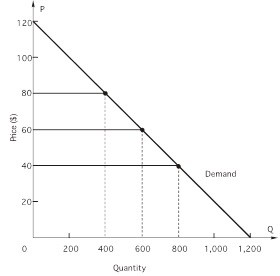 In the figure above, if price DECREASES from $80 to $60, an arrow representing the QUANTITY effect
In the figure above, if price DECREASES from $80 to $60, an arrow representing the QUANTITY effect
A. will be shorter than (and in the same direction of) the arrow representing the price effect. B. will point in the opposite direction in which total revenue will move. C. will be shorter than (and in the opposite direction of) the arrow representing the price effect. D. will point upward. E. will point downward.