The "law of demand" is illustrated by a
A) rightward shift of the demand curve.
B) leftward shift of the demand curve.
C) movement along the demand curve.
D) Both answers A and B are correct.
C
You might also like to view...
An example of how economic growth might not lead to economic development is:
A. the rate of literacy increased among all groups when a nation’s economy grew. B. people had greater social mobility due to the growth experienced in the nation. C. the average income in a nation increased with greater GDP growth. D. when a nation’s economy grew, the rate of malnutrition among children was relatively constant.
The greater the magnitude of the external benefits of production, a. The larger is the deadweight loss from underproduction
b. The greater would be the optimal subsidy. c. The further the private market solution ignoring those benefits would deviate from the socially efficient level of output. d. All of the above are true
A. panel (b) only. In panel (b), there will be
A. a shortage of wheat. B. a surplus of wheat. C. equilibrium in the market. D. lines of people waiting to buy wheat.
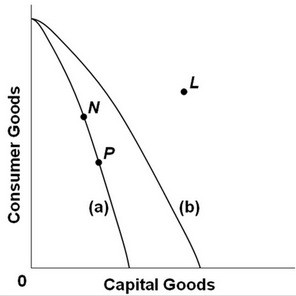 Refer to the above production possibilities curves. Curve (a) is the current curve for the economy. Other things being equal, society's current choice of point P on curve (a) will:
Refer to the above production possibilities curves. Curve (a) is the current curve for the economy. Other things being equal, society's current choice of point P on curve (a) will:
A. entail a slower rate of economic growth than would the choice of point N. B. be unobtainable because it exceeds the productive capacity of the economy. C. allow it to achieve more rapid economic growth than would the choice of point N. D. entail the same rate of growth as would the choice of point N.