If labor productivity growth slows down in a country, this means that the growth rate in ________ has declined
A) the quantity of goods or services that can be produced by one hour of work
B) nominal GDP
C) labor force participation
D) the working-age population
Article Summary
According to the Office for National Statistics in the United Kingdom, productivity in the UK in 2014 was well below the average of the G7 countries, only faring better than Japan. The G7 is a group of the seven most industrialized countries, and includes Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Compared to the G7 average, the UK was 20% less productive per hour worked, and output was also 20% worse when measured on a per worker basis. The productivity gap was the largest for the UK since estimates began in 1991. Worker productivity was lower in all of the G7 nations in 2014 than it would have been had trends prior to the 2007-2009 recession continued, with the productivity gap of 18 percent in the UK significantly higher than the 7% gap for the other G7 nations. In terms of output per hour worked, the UK was behind Germany, France, and the United States by 32 to 33 percentage points.
Source: "UK's poor productivity figures show challenge for government," Guardian, September 18, 2015.
A
You might also like to view...
Investment treaties usually do not cover
a. repatriation of funds b. nationalization c. arbitration of disputes d. reciprocal tax treatment e. treaties generally cover all of the above
Interest rates and investment are actually observed to move most of time in ________, and this is explained by other factors affecting investment shifting the ________ curve to the right
A) the same direction, IS B) the same direction, LM C) opposite directions, IS D) opposite directions, LM
A labor union is a(n)
a. single seller of labor on the labor market b. single buyer of labor on the labor market c. organization of workers who produce goods that are sold in union shops d. organization of workers who typically strike to obtain high wage rates e. organization of workers who refuse to work unless they are paid a wage rate above MRP
Refer to the above graphs. A price increase from $20 to $40 causes quantity demanded to decrease from 100 units to 50 units. Which graph best illustrates the price elasticity of demand for this good?
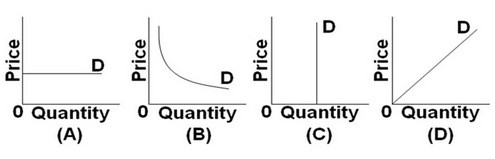
A. Graph A
B. Graph B
C. Graph C
D. Graph D