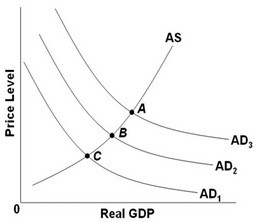
 Refer to the above diagram. The economy is at equilibrium at point C. What fiscal policy would increase real GDP?
Refer to the above diagram. The economy is at equilibrium at point C. What fiscal policy would increase real GDP?
A. Increase aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 by increasing government spending.
B. Make no change because the economy is at or near its full-employment level of real output.
C. Increase aggregate demand from AD2 to AD1 by decreasing taxes.
D. Decrease aggregate demand from AD2 to AD3 by increasing taxes.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If a firm reacts to other firms' market decisions by anticipating how the others will then react, this reflects
a. the behavior of followers of a price leader b. the behavior associated with price leadership c. a market with a low concentration ratio d. mutual interdependence e. collusion by definition
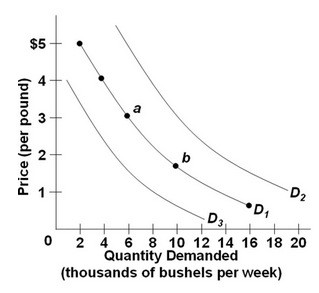 Refer to the above diagram, which shows three demand curves for coffee. Which would cause the change in the demand for coffee illustrated by the shift from D1 to D2?
Refer to the above diagram, which shows three demand curves for coffee. Which would cause the change in the demand for coffee illustrated by the shift from D1 to D2?
A. An increase in consumer incomes B. An increase in the price of sugar C. A decrease in the price of tea D. A technological improvement in the production of coffee
The demand for a resource rises as
A. its productivity rises and the relative prices of substitutable resources rise. B. its productivity rises and prices of substitutable resources fall. C. its productivity falls and the relative prices of substitutable resources fall. D. its productivity falls and prices of substitutable resources fall.
The shape of the immediate-short-run aggregate supply curve implies that:
A. total output depends on the volume of spending. B. increases in aggregate demand are inflationary. C. output prices are flexible, but input prices are not. D. government cannot bring an economy out of a recession by increasing spending.