Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 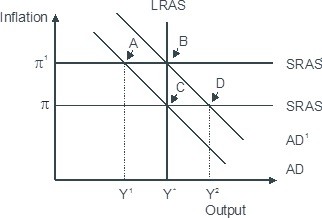
A. D; an expansionary
B. B; no output
C. B; expansionary
D. A; a recessionary
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The following table shows the relationship between the speed of a computer's CPU and its benefits and costs. Assume that all other features of the computer are the same (that is, CPU speed is the only source of variation), and only the CPU speeds listed below are available for purchase.CPUGHzTotal BenefitMarginal BenefitTotal CostsMarginal Costs2.0$1,000 $900 2.5$1,400 &1003.0 $300$1,200 3.5$1,900 &1,500 4.0$2,000 &400The total cost of a 2.5GHz computer is:
A. $200. B. $900. C. $1,000. D. $100.
In 1914, Henry Ford increased his workers’ wages from $3 to $5 per day and succeeded in increasing his profits. Which of the following principles was he demonstrating?
a. efficiency wage b. relative price c. natural rate of unemployment d. potential output
If excessive aggregate demand causes prices to rise, which of the following would be a correct fiscal-policy action?
A. An increase in government expenditures B. An increase in the money supply C. An increase in Social Security payments D. A tax increase
In the traditional Keynesian model, a decrease in government spending lowers total planned real expenditures by more than the original decrease in government spending because
A. of the crowding-out effect on consumption spending. B. consumption spending depends positively on real GDP. C. consumption spending depends negatively on real GDP. D. consumption spending is not related to real GDP.