How can firms survive in the long run if mandatory retirement is illegal and if firms are stuck with older workers whose productivity might technically have fallen over time?
What will be an ideal response?
The way to deal with this is to ensure seniority rules, which create among the existing younger workers a sense of loyalty to the firm. More subtly, the firm can underpay you when you are young and slowly increase your payment as you attain seniority. The present value of your lifetime earnings then is basically equal to the present value of your productivity, and the firm is not hurt in the long run.
You might also like to view...
In terms of efficiency, trade diversion is a _____ desirable outcome of a regional free-trade agreement, because trade is diverted from the ___________ producer to the __________ producer .
a. more; high-cost; low-cost b. more; less deserving; more deserving c. less; low-cost; high-cost d. less; foreign; domestic
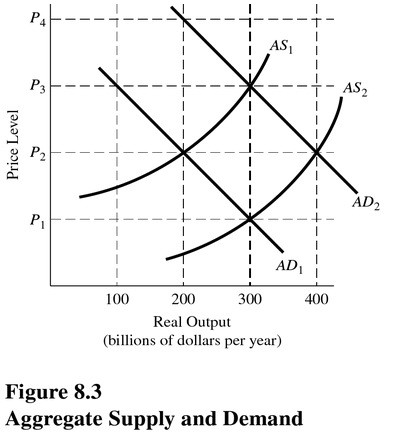 Assume the economy is initially in equilibrium on AD1 and AS1. Which curve would have shifted, and in what direction would it have shifted, if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of $300 billion and a price level of P3 in Figure 8.3?
Assume the economy is initially in equilibrium on AD1 and AS1. Which curve would have shifted, and in what direction would it have shifted, if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of $300 billion and a price level of P3 in Figure 8.3?
A. Aggregate demand would have shifted to the left. B. Aggregate supply would have shifted to the right. C. Aggregate demand would have shifted to the right. D. Aggregate supply would have shifted to the left.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.6 below to answer the question(s) that follow.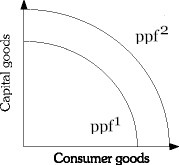 Figure 2.6Refer to Figure 2.6. If the economy is at ppf2, a change in consumer taste would be shown by a
Figure 2.6Refer to Figure 2.6. If the economy is at ppf2, a change in consumer taste would be shown by a
A. movement along ppf1. B. movement along ppf2. C. shift from ppf2 to ppf1. D. shift from ppf1 to ppf2.
When the interest rate rises, bond values
A. rise. B. fall. C. will either increase or decrease depending on the type of bond. D. are unchanged because the interest rate paid on a bond is fixed.