To find the social marginal benefit of public goods, one needs to
A) sum the consumers' demand curves vertically.
B) sum the consumers' demand curves horizontally.
C) sum the marginal private benefit and the marginal external benefit for each unit.
D) sum the marginal private cost and the marginal external cost for each unit.
E) subtract the individual portion of the tax burden necessary for the government to provide the good from the demand curve of each consumer who desires the good.
A
You might also like to view...
Player 1 and Player 2 are playing a game in which Player 1 has the first move at A in the decision tree shown below. Once Player 1 has chosen either Up or Down, Player 2, who can see what Player 1 has chosen, must choose Up or Down at B or C. Both players know the payoffs at the end of each branch. 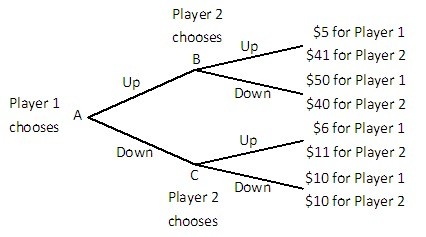 If Player 2 could make a credible commitment to choose either Up or Down when his or her turn came, then what would Player 2 do?
If Player 2 could make a credible commitment to choose either Up or Down when his or her turn came, then what would Player 2 do?
A. Player 2 would commit to choosing Down. B. Player 2 would commit to choosing Up. C. Player 2 would not commit to choosing either strategy. D. Player 2 would commit to mimicking Player 1's strategy.
A simple linear demand function may be stated as Q = a - bP + cI where Q is quantity demanded, P is the product price, and I is consumer income. To compute an appropriate value for b, we can use observed values for Q and P and then set -b(P/Q) equal to the:
A. cross-price elasticity of demand. B. price elasticity of supply. C. income elasticity of demand. D. price elasticity of demand.
Who is included in the labor force by the Bureau of Labor Statistics?
a. Tina, who worked most of the week in a steel factory b. Kelly, who is temporarily laid off but expects to be recalled c. DJ, who does not have a job but is looking for work d. All of the above are correct.
Fiscal policy affects the goods market through
A. changes in taxes and government spending. B. changes in taxes and money supply. C. changes in government spending and money supply. D. changes in money supply.