When a small spherical rock of radius r falls through water, it experiences a drag force (a)(r)(v), where "v" is its velocity and "a" is a constant proportional to the viscosity of water
From this, one can deduce that if a rock of diameter 2 mm falls with terminal velocity, "v," then a rock of diameter 4 mm will fall with terminal velocity A) v / 4.
B) 2 v.
C) v / 2.
D) 4 v.
E) v.
D
You might also like to view...
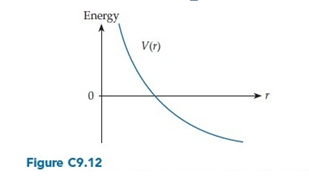 Figure C9.12 shows the potential energy function for a certain interaction. This interaction is
Figure C9.12 shows the potential energy function for a certain interaction. This interaction is
A. Always attractive. B. Always repulsive. C. Attractive for small r, but repulsive for large r. D. Repulsive for small r, but attractive for large r.
The average intensity of the sunlight in Miami, Florida, is 1060 W/m2. What is the average value of the force exerted on a 16m2 surface that absorbs this light?
A) 7.83 × 10-5 N B) 1.63 × 10-5 N/m2 C) 2.61 × 10-5 N D) 5.65 × 10-5 N E) 0.204 × 10-5 N
A gravitational lens occurs when
A) a massive object causes more distant objects to appear much larger than they should, and we can observe the distant objects with better resolution. B) a telescope lens is distorted by gravity. C) a massive object bends light beams that are passing nearby. D) dark matter builds up in a particular region of space, leading to a very dense region and an extremely high mass-to-light ratio.
The banking angle for a properly banked curve does not depend on the mass of the car going over it
Indicate whether the statement is true or false