The biological species concept:
a. states that any organisms that are biologically similar constitute a species.
b. states that a species is any group that shares similar DNA.
c. is infrequently used because it is inapplicable to many organisms.
d. defines a species as any group of actually or potentially interbreeding species that produce viable offspring.
e. is the best and most accurate species concept.
Ans: d. defines a species as any group of actually or potentially interbreeding species that produce viable offspring.
You might also like to view...
Tetherin is a protein encoded in the human genome. Based on what you know about the interaction between Vpu and tetherin, what do you predict the broad cellular function of tetherin is?
A. To keep HIV particles in place until they are ready to bud B. To stop the spread of HIV in the body by inhibiting HIV release C. To help in HIV assembly D. To help with the maturation of HIV particles
The number of generations it takes for an allele to become fixed or lost in a population depends on population size. There are three populations associated with the frequency of the ? allele and its change in frequency. Which population(s) show dramatic change in ? allele frequency and what are these changes? Population 1 = brown mouse (top line); Population 2 = middle line; population 3 =
white mouse (bottom line).
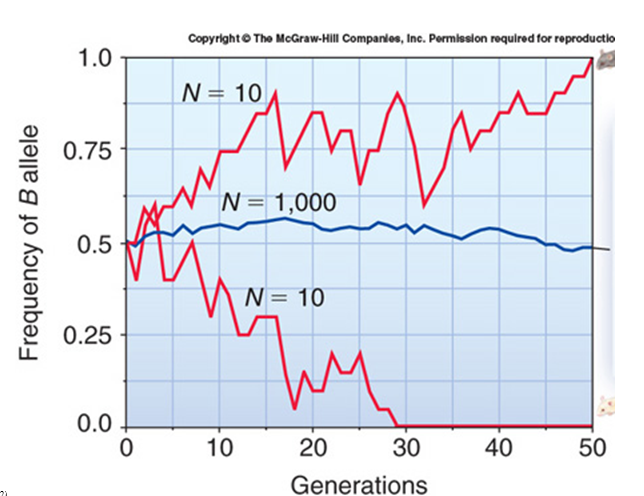
A. Population 1; it shows an extinction of the ? allele resulting in all brown mice.
B. Population 3; it shows an extinction of the ? allele resulting in all white mice.
C. Population 2; it shows an increase in the frequency of the ? allele after 50 generations.
D. Population 1; it shows a fixation of the ? allele resulting in all brown mice and Population 3 shows an extinction of the ? allele resulting in all white mice.
E. Population 1, 2, and 3 all show drastic changes in ? allele frequency after 50 generations, with the complete elimination of the ? allele in all three populations.
The protein SOS is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Ras. SOS helps facilitate the exchange of GDP for GTP. What would be the effect of a mutation that inhibits the interaction between SOS and Ras?
A. GTP would remain bound to Ras, thereby keeping Ras constitutively active. B. GDP would remain bound to Ras, thereby preventing Ras activation. C. Ras would be more likely to hydrolyze GTP to GDP. D. There would be no effect.
Salmon fisheries are located in the coastal waters of:
a. Alaska. b. New England. c. the Pacific Northwest. d. China. e. both a and c