The trade-off between current consumption and the production of capital goods is also a trade-off between
A) the future cost for capital goods and future cost of consumption goods.
B) having fewer needs and more wants in the future.
C) satisfying the needs of the poor and the wants of the wealthy.
D) current consumption and future consumption.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The unemployment rates during the last 10 years in the Eurozone was
A) constantly lower than the unemployment rate in the United States and not rising toward the U.S. unemployment rate. B) constantly lower than the unemployment rate in the United States but were rising toward the U.S. unemployment rate. C) more or less constant at 3 percent. D) generally higher than the U.S. unemployment rate. E) approximately equal to those in the United States, with some years the U.S. unemployment rate being slightly higher and in other years the U.S. unemployment rate being slightly lower.
Assuming the firm in the graph shown is producing Q1 and charging P3, it is likely showing the cost and revenue curves of a monopolistically competitive firm that is:
These are the cost and revenue curves associated with a firm.
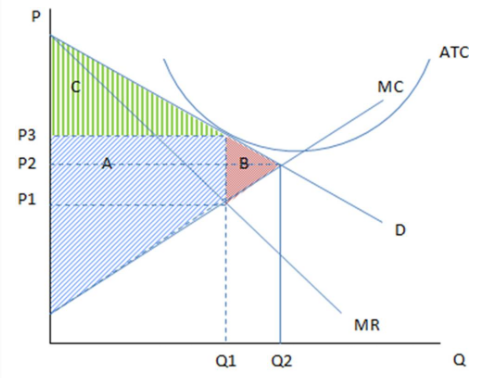
A. earning positive economic profits.
B. earning negative economic profits.
C. earning zero economic profits.
D. It is impossible to tell from the graph provided.
In the classical model, the supply of funds to the loanable funds market comes from
a. household saving and the government's budget surplus, if any b. net taxes c. household saving and the government budget deficit, if any d. planned investment e. total income
A way in which government can attempt to solve the problems caused by information asymmetry in the marketplace is:
A. screening. B. building a reputation. C. disclosure laws. D. statistical discrimination.