In the figure below, spending $1 million on advertising increases the demand from D0 to D1. The gross average cost curve, LACGROSS, excludes the cost of the advertising. Before the firm advertised, the profit-maximizing price and quantity were ________ and after the firm advertised the profit-maximizing price and quantity are ________
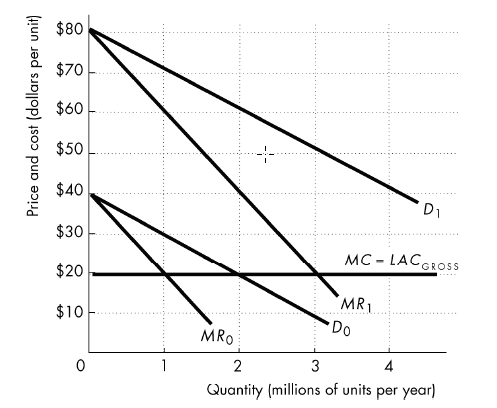
A) $30 per unit and 1 million units; $50 per unit and 3 million units
B) $20 per unit and 2 million units; $60 per unit and 2 million units
C) $20 per unit and 1 million units; $20 per unit and 3 million units
D) $30 per unit and 1 million units; It is impossible to tell because the cost of the advertising is not included in the gross average cost.
A) $30 per unit and 1 million units; $50 per unit and 3 million units
You might also like to view...
The RBC model tells us that
A) as the real wage rate rises, the amount of labor supplied and thus output produced falls. B) as the price level rises, the real wage rises, thus raising the amounts of labor supplied and output produced. C) as the real interest rate rises, the amount of labor supplied and thus output produced rises. D) as the price level rises above the expected price level, actual output rises above the natural real GDP.
When the inflation rate rises, the purchasing power of nominal income:
a. remains unchanged. b. decreases. c. increases. d. changes by the inflation rate minus one.
A price floor is a reasonable price control mechanism to impose in cases where the government believes the market's equilibrium price
a. creates an excess supply that will force price downward b. is too high c. creates an excess demand that will force price upward d. is too low e. is higher than the market price
In 2010, the co-chairmen of President Obama's deficit reduction commission proposed curtailing or eliminating many tax deductions such as the one for mortgage interest. Economists who favor the proposal argue that it would (i) correct a misallocation of resources because too much of the economy's capital stock is tied up in residential housing and too little is invested in corporate capital. (ii)
cut both spending and taxes. (iii) encourage private philanthropy. a. (i) only b. (ii) only c. (i) and (ii) only d. (i), (ii), and (iii)