The gravitational lens effect has been verified by
A) observations of multiple images of the same background galaxy seen towards a massive galaxy cluster.
B) single images of highly distorted, high-redshift galaxies seen towards massive galaxy clusters.
C) observations of the bending of starlight by the Sun during a 1919 eclipse.
D) all of the above
E) None of the above; this effect is purely hypothetical.
D
You might also like to view...
During the Planck Epoch, all forces were ________, and the universe was considered as a singularity
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Energy Conservation With Nonconservative Forces: As shown in the figure, a 1.45-kg block is held in place against the spring by a 21-N horizontal external force. The external force is removed, and the block is projected with a velocity v1 = 1.2 m/s as it separates from the spring. The block descends a ramp and has a velocity v2 = 2.1 m/s at the bottom. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The block enters a rough section at B, extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the rough surface is 0.29. The velocity of the block is v3 = 1.4 m/s at C. The block moves on to D, where it stops. How much work is done by friction between points B and C?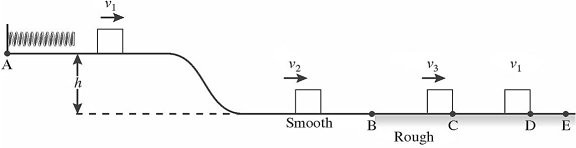
style="vertical-align: 0.0px;" height="148" width="576" /> A. -1.8 J B. -3.6 J C. -14 J D. -6.4 J E. -7.0 J
Two lights are 1000 ns apart along a stretch of railway track. In the ground frame, the west light flashes 600 ns before the east light flashes. Could these flashes be simultaneous in the frame of a train moving along the track at a certain speed (that is less than the speed of light)?
A. Yes, if the train is moving east at the correct speed. B. Yes, if the train is moving west at the correct speed. C. Yes, if the train observer happens to be at the right distances from the lights when receiving their flashes. D. No, the flashes cannot be simultaneous in any frame.
A particle and its antiparticle have:
a. the same mass and the same electric charge. b. the same mass and equal charge of opposite sign. c. equal mass of opposite sign, and equal charge of opposite sign. d. equal mass of opposite sign, and the same charge. e. mass and charge that are unrelated from one particle to the other.